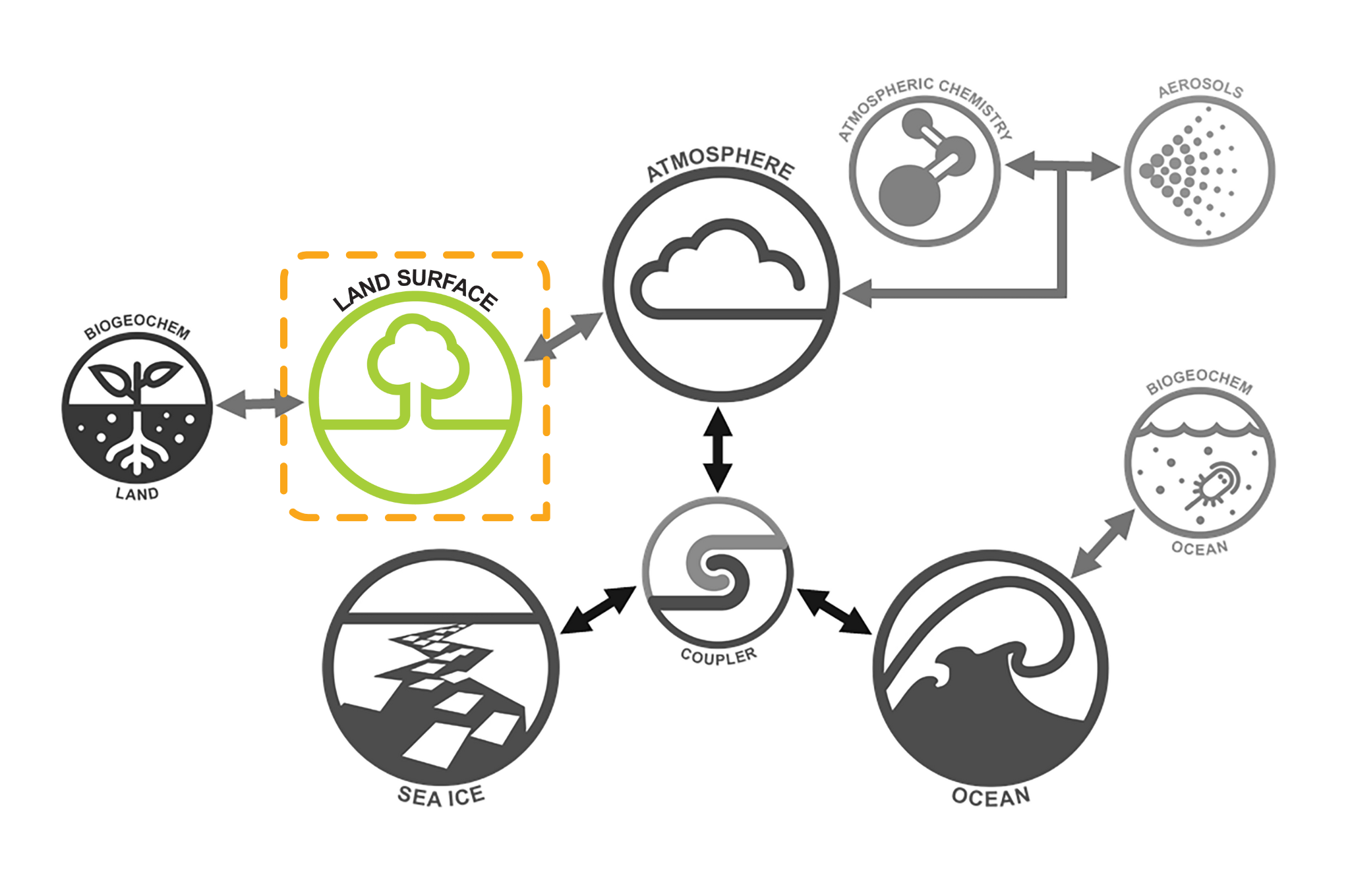
Land Surface component
CABLE
Community Atmosphere Biosphere Land Exchange (CABLE) is a land surface model used to calculate the fluxes of momentum, energy, water and carbon between the land surface, vegetation canopy and the atmospheric boundary layer. It also includes descriptions of thermal and hydrological processes in the soil and snow, and models the main biogeochemical cycles of the land ecosystem when used in conjunction with the CASA-CNP module.
CABLE is an open source model developed by a community of Australian climate science researchers.
Refer to CABLE documentation to know how to work with the CABLE model.
Model configurations that use CABLE
- ACCESS-CM2 (directly coupled into the UM)
- ACCESS-ESM1.5 (directly coupled into the UM)
CABLE can also be run as a standalone model.
Benchcab: evaluation tool for CABLE
Benchcab is a testing framework tool for CABLE. It allows to test CABLE's scientific performance across a range of model configurations and model versions.
The tool currently works with the following configurations for CABLE:
- Flux site simulations (offline)
running CABLE forced with observed eddy covariance data at a single site - Global/regional simulations (offline)
running CABLE forced with meteorological fields, globally or over a region
The output of these simulations can then be uploaded to modelevaluation.org for a statistical analysis of the scientific performance of the supplied configurations.
To learn more about benchcab, its functionalities and limitations, refer to benchcab's documentation.
JULES
The Joint UK Land Environment System (JULES) is a community land surface model that can be used both as a standalone model and as the land surface component in the UM model. By modelling different land surface processes (surface energy balance, hydrological cycle, carbon cycle, dynamic vegetation, etc.) and their interaction with each other, JULES provides a framework to assess the impact of modifying a particular process on the ecosystem as a whole, for example the impact of climate change on hydrology.
Model configurations that use JULES
Other ACCESS models used for weather simulations, not supported by ACCESS-NRI, use JULES. Examples are ACCESS-S and ACCESS-C developed by the Bureau of Meteorology (BoM).