ACCESS-CM
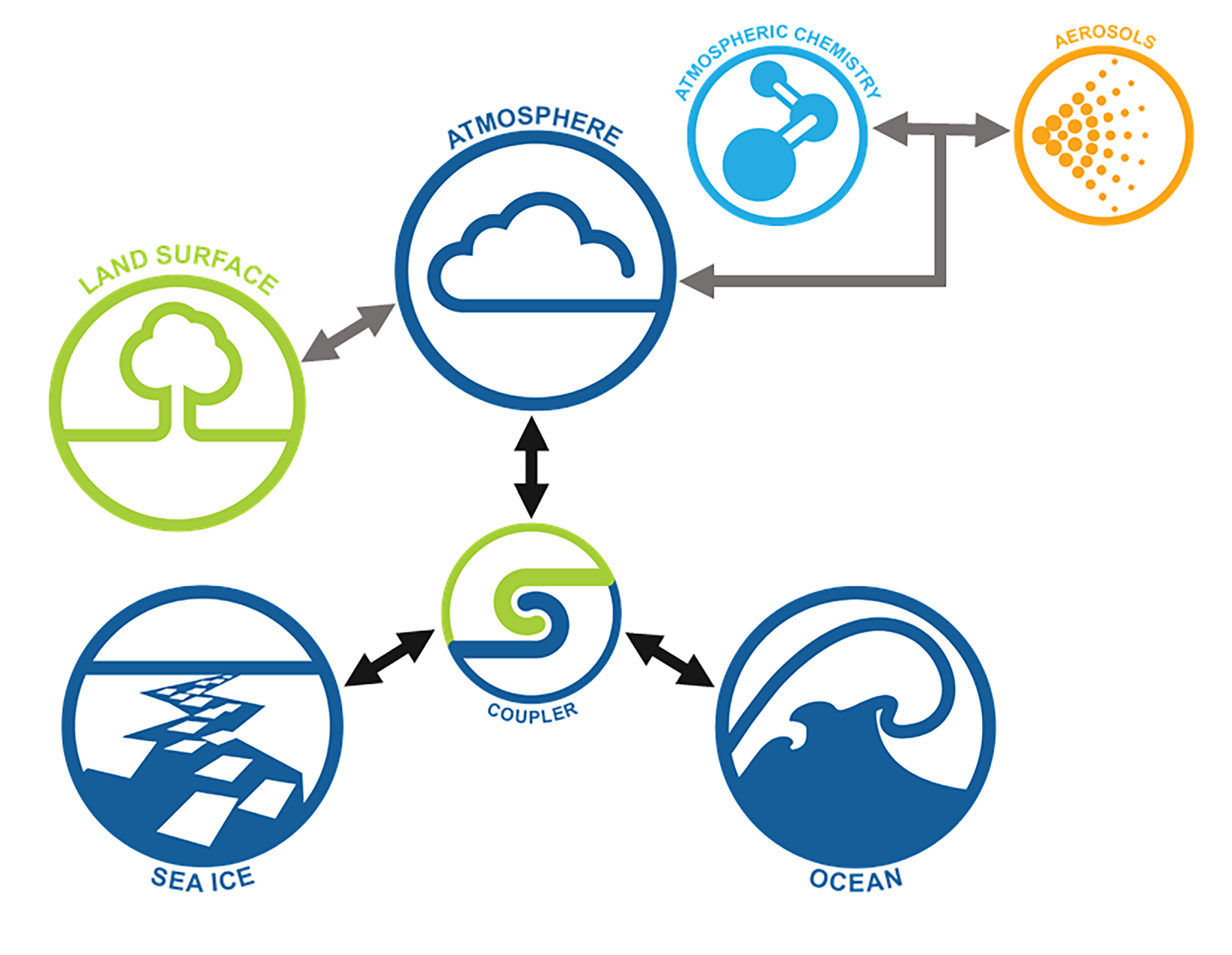
The ACCESS Coupled Model (ACCESS-CM) is a fully-coupled global climate model that includes atmosphere, aerosols and atmospheric chemistry, land, ocean and sea ice components, linked together by a coupler.
It produces physical climate simulations.
ACCESS-CM2
ACCESS-CM2 1 was initially developed by CSIRO and is one of Australia’s contributions to the World Climate Research Programme’s Coupled Model Intercomparison Project Phase 6 (CMIP6).
Model components
-
Atmosphere: UM10.6, GA7.1 science configuration.
N96 spatial resolution (1.875° x 1.25°), 85 vertical levels. Physical model only – no carbon cycle. -
Aerosols and Atmospheric Chemistry: GLOMAP for the aerosols and UKCA for the atmospheric chemistry.
-
Land: CABLE2.5.
-
Ocean: MOM5.
Tripolar grid, 1° spatial resolution, 50 vertical levels. -
Sea ice: CICE5.1.2.
Same grid as Ocean. -
Coupler: OASIS3-MCT.
Compared to previous model versions, ACCESS-CM2 shows better global hydrological balance, more realistic ocean water properties (in terms of spatial distribution) and meridional overturning circulation in the Southern Ocean. It does, however, produce a poorer simulation of the Antarctic sea ice and a larger energy imbalance at the top of atmosphere. ACCESS-CM2 has a relatively high equilibrium climate sensivity of 4.7°C for doubled CO2 concentration.
-
Daohua Bi, Martin Dix, Simon Marsland, Siobhan O'Farrell, Arnold Sullivan, Roger Bodman, Rachel Law, Ian Harman, Jhan Srbinovsky, Harun A Rashid, Peter Dobrohotoff, Chloe Mackallah, Hailin Yan, Anthony Hirst, Abhishek Savita, Fabio Boeira Dias, Matthew Woodhouse, Russell Fiedler, and Aidan Heerdegen. Configuration and spin-up of ACCESS-CM2, the new generation Australian Community Climate and Earth System Simulator coupled model. Journal of Southern Hemisphere Earth Systems Science, 70(1):225–251, 2020. doi:10.1071/ES19040. ↩